Tổng hợp các đề thi thử THPT quốc gia môn tiếng anh năm 2021 cho các bạn tham khảo luyện thi:
Category: Đề thi
Đề thi mẫu tiếng Anh THPT Quốc gia 2021 của Bộ GD&ĐT
Đề thi mẫu THPT quốc gia năm 2021 môn tiếng Anh của Bộ giáo dục và đào tạo vẫn gồm 5 kỹ năng với 50 câu: Ngữ âm, ngữ pháp, giao tiếp, đọc, và viết. Mọi người cùng tham khảo đề thi mẫu dưới đây:
Tải file PDF Đề thi mẫu tiếng Anh THPT Quốc gia 2021 của Bộ GD&ĐT





Đáp án Đề thi mẫu tiếng Anh THPT Quốc gia 2021 của Bộ GD&ĐT
| 1. B | 2. A | 3. D | 4. A | 5. D | 6. B | 7. A | 8. B | 9. C | 10. A |
| 11. D | 12. A | 13. A | 14. A | 15. C | 16. A | 17. A | 18. B | 19. A | 20. B |
| 21. A | 22. A | 23. A | 24. A | 25. B | 26. B | 27. A | 28. B | 29. C | 30. B |
| 31. | 32. D | 33. D | 34. C | 35.A | 36. | 37. A | 38.B | 39. B | 40. A |
| 41. | 42. | 43. B | 44. D | 45. D | 46. A | 47. C | 48. A | 49. B | 50. D |
Đề thi mẫu THPT Quốc gia môn tiếng Anh năm 2020
Đề thi mẫu THPT quốc gia năm 2020 môn tiếng anh vẫn gồm 50 câu hỏi chia thành 5 kỹ năng: Ngữ âm, ngữ pháp, giao tiếp, đọc, và viết. Mọi người cùng tham khảo đề thi mẫu dưới đây:
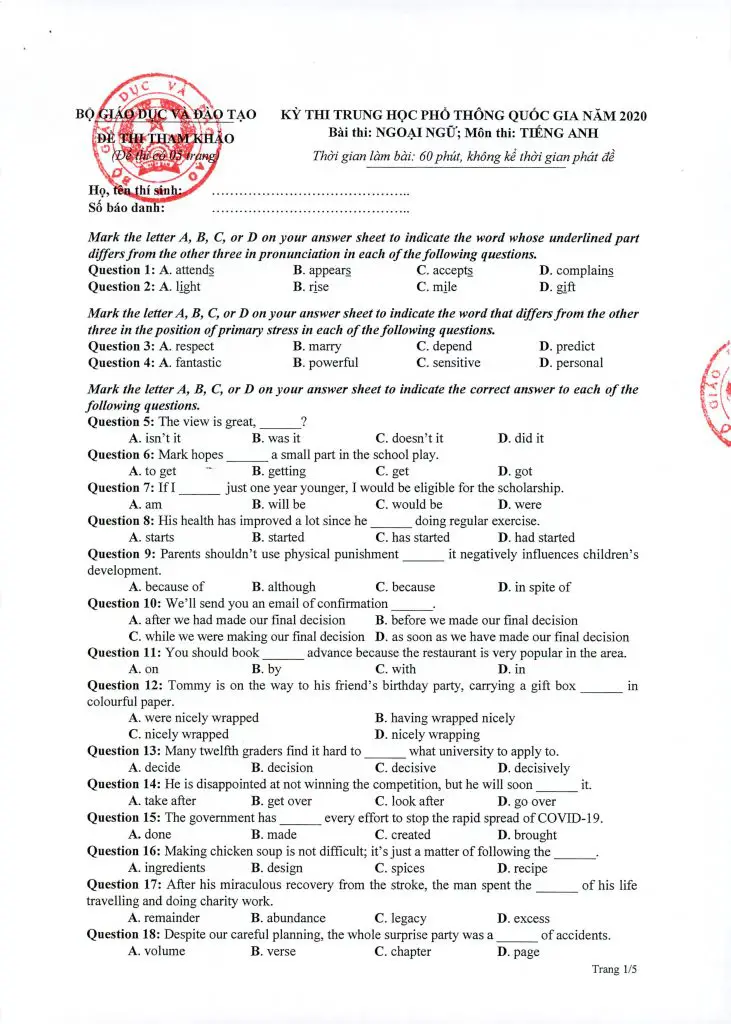




Cấu trúc đề thi THPT Quốc gia môn tiếng Anh năm 2020
Cấu trúc đề thi THPT Quốc gia môn tiếng Anh năm 2020 có thể giống như các năm gồm 5 kỹ năng chính chia làm 5 phần.
Ma trận đề thi
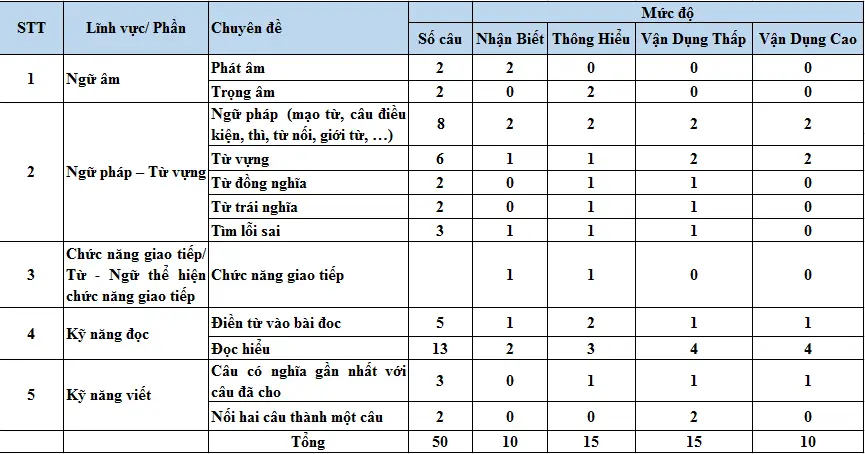
1. Kỹ năng Ngữ âm
Ngữ âm gồm 2 phần: phát âm và trọng âm kiểm tra kỹ năng tìm trọng âm của từ và cách phát âm các từ tiếng Anh. Phần này có khoảng 4 câu.
Ví dụ câu về phát âm:
Mark the letter A, B, C, or D on your answer sheet to indicate the word whose underlined part differs from the other three in pronunciation in each of the following questions.
A. blood B. food C. mood D. but
Ví dụ câu về trọng âm:
Mark the letter A, B, C, or D on your answer sheet to indicate the word that differs from the rest in the position of the primary stress in each of the following questions.
A. argument B. admission C. domestic D. acquaintance
2. Kỹ năng Ngữ pháp, từ vựng
Ngữ pháp có 8 câu hỏi gồm các loại như mạo từ, câu điều kiện, từ nối, giới từ
Từ vựng 10 câu hỏi, từ đồng nghĩa 2 câu, từ trái nghĩa 2 câu, tìm lỗi sai 3 câu.
Ví dụ câu về ngữ pháp
Mark the letter A, B, C, or D on your answer sheet to indicate the correct answer to each of the following questions.
If you ________a wallet in the street, what would you do with it?
A. found B. have found C. find D. had found
Ví dụ câu về từ vựng:
Mark the letter A, B, C, or D on your answer sheet to indicate the sentence that is CLOSEST in meaning to each of the following questions.
The news surprised everyone in the family.
A. Everyone in the family found the news surprising.
B. The news in the family made everyone surprisingly.
C. The news made everyone surprised in the family.
D. Everyone was surprised by the news in the family.
3. Chức năng giao tiếp
Gồm các câu hỏi liên quan đến Từ – Ngữ thể hiện chức năng giao tiếp
Ví dụ câu chức năng giao tiếp
Mark the letter A, B, C, or D on your answer sheet to indicate the most suitable response to complete each of the following exchanges.
Mark: “Why do you like red color?”
Mark’s brother: “ ____________________”
A. You make me feel more confident. B. It’s a good idea, thank you.
C. It’s the color of love and passion. D. You didn’t do anything for me.
4. Kỹ năng đọc
Kỹ năng đọc gồm kỹ năng điền từ vào chỗ trống 5 câu, đọc hiểu 13 câu
Ví dụ câu điền vào chỗ trống
Read the following passage and mark the letter A, B, C, or D on your answer sheet to indicate the correct word or phrase that best fits each of the numbered blanks.
Monkeys are similar to humans in many ways. For example, the (7)__________in a monkey family, such as between brother and sister, are often very close. A team of researchers studied a pair of bonobo monkeys called Kanzi and Panbanisha. (8)___________brother and sister team had learned how to make knives from stone. So the researchers decided to record how good they were. The researchers put a banana inside a box. Then they gave the bonobos what they needed to make knife. The (9)__________of this knife was to cut open the box to get the banana. Kanzi made a very good knife, but his sister Panbanisha could not. Kanzi saw his sister was feeling (10)___________and so he tried to give his knife to her. However, the scientists did not let him. Even in this situation, Kanzi knew what to do. When no one was looking, he put his knife (11)__________ his sister could easily find it, and she finally got her banana. To researchers, it was obvious from Kanzi’s behavior that he really wanted to help his sister.
Câu 7 (TH): A. relatives B. relation C. relate D. relationships
Câu 8 (NB): A. Those B. The C. These D. A
Câu 9 (TH): A. performance B. usage C. function D. application
Câu 10 (TH): A. disappointing B. disappointed C. disappointment D. disappoint
Câu 11 (TH): A. where B. how C. that D. what
Ví dụ câu đọc hiểu
Read the passage and mark the letter A, B, C, or D on your answer sheet to indicate the correct answer to each of the questions.
In today’s competitive world, what responsible parents would not want to give their children the best possible start in life? For this reason, many parents want their children, often as young as ten months old, to become familiar with computers. They seem to think that if their children grow up with computers, they will be better equipped to face the challenges of the future.
No one has proved that computers make children more creative or more intelligent. The truth may even be the opposite. Educational psychologists claim that too much exposure to computers, especially for the very young, may negatively affect normal brain development. Children gain valuable experience of the world from their interaction with physical objects. Ten-month-old babies may benefit more from bumping their heads or putting various objects in their mouths than they will from staring at eye-catching cartoons. A four-year-old child can improve hand-eye coordination and understand cause and effect better by experimenting with a crayon than by moving a cursor around a computer screen. So, as educational psychologists suggest, instead of government funding going to more and more computer classes, it might be better to devote resources to music and art programs.
It is ludicrous to think that children will fall behind if they are not exposed to computers from an early age. Time is too precious to spend with a “mouse”. Now is the time when they should be out there learning to ride a bike. There will be time later on for them to start banging away at keyboards.
Children who spend a lot of time on their computers _________.
A. will suffer from brain damage
B. do not necessarily make more progress than those who don’t
C. tend to have more accidents than those who don’t
D. tend to like music and art more than those who don’t
5. Kỹ năng viết
Bao gồm các kỹ năng tìm câu có nghĩa gần nhất với câu đã cho 3 câu hỏi. Nối 2 câu thành 1 câu với 2 câu hỏi.
Ví dụ câu kỹ năng viết
Mark the letter A, B, C, or D on your answer sheet to indicate the word(s) CLOSEST in meaning to the underlined word(s) in each of the following questions.
Every time he opens his mouth, he immediately regrets what he said. He is always putting his foot in his mouth.
A. speaking indirectly B. saying embarrassing things
C. doing things in the wrong order D. making a mistake
Tổng số câu và thời gian làm bài
Tổng số câu của đề thi là 50 câu.
Thời gian làm bài: 60 phút
Thi thử THPT Quốc gia môn tiếng Anh tại đây
Thi thử tiếng anh THPT Quốc gia năm 2020
Cấu trúc đề thi tiếng anh THPT Quốc gia
Phần 1: Ngữ âm
Ngữ âm gồm 2 phần: phát âm và trọng âm kiểm tra kỹ năng tìm trọng âm của từ và cách phát âm các từ tiếng Anh. Phần này có khoảng 4 câu.
Phần 2: Ngữ pháp, từ vựng
Ngữ pháp có 8 câu hỏi gồm các loại như mạo từ, câu điều kiện, từ nối, giới từ
Từ vựng 10 câu hỏi, từ đồng nghĩa 2 câu, từ trái nghĩa 2 câu, tìm lỗi sai 3 câu.
Phần 3: Chức năng giao tiếp
Gồm các câu hỏi liên quan đến Từ – Ngữ thể hiện chức năng giao tiếp
Phần 4: Kỹ năng đọc
Kỹ năng đọc gồm kỹ năng điền từ vào chỗ trống 5 câu, đọc hiểu 13 câu
Phần 5: Kỹ năng viết
Bao gồm các kỹ năng tìm câu có nghĩa gần nhất với câu đã cho 3 câu hỏi. Nối 2 câu thành 1 câu với 2 câu hỏi.
Tổng số câu của đề thi là 50 câu.
Thời gian làm bài: 60 phút
Đề thi thử online
Thi thử tiếng anh THPT Quốc gia năm 2020 với các đề dưới đây:
Tổng hợp các đề thi thử THPT Quốc gia môn Tiếng Anh năm 2020
Giới thiệu
Thi THPT Quốc gia là kỳ thi đặc biệt quan trọng đối với các bạn học sinh lớp 12 để bước vào cánh cửa đại học. Để chuẩn bị tốt cho kỳ thi này đặc biệt là môn Tiếng Anh các bạn nên tìm và luyện tập các đề thi thử để rèn luyện trước khi vào kỳ thi chính thức.
Cấu trúc đề thi
Đề thi THPTQG gồm các phần:
Ngữ âm: gồm có phát âm và trọng âm số câu mỗi loại 2 câu
Ngữ pháp – từ vựng: gồm ngữ pháp, từ vựng, từ đồng nghĩa, từ trái nghĩa, tìm lỗi sai
Chức năng giao tiếp
Kỹ năng đọc: điền từ vào bài đọc, đọc hiểu
Kỹ năng viết: Câu gần nghĩa với câu đã cho, nối 2 câu thành 1 câu
Tổng hợp các đề thi thử THPT Quốc gia môn tiếng anh năm 2020
Đề thi thử Tiếng anh THPT Quốc gia năm 2020 tỉnh Bắc Ninh
SỞ GD & ĐT BẮC NINH PHÒNG QUẢN LÝ CHẤT LƯỢNG
Mã đề thi 323
ĐỀ TẬP HUẤN THI THPT QUỐC GIA NĂM 2020 MÔN: TIẾNG ANH
Thời gian làm bài: 60 phút; không kể thời gian phát đề
Phần 1
Mark the letter A, B, C, or D on your answer sheet to indicate the word(s) CLOSEST in meaning to the underlined word(s) in each of the following questions from 1 to 2.
Câu 1 (VDC): Although we argued with him for a long time, he stood his ground.
A. felt sorry for us B. changed his decision
C. refused to change his decision D. wanted to continue
Câu 2 (TH): English, Maths and Literature are core subjects, which are compulsory in the national examination.
A. minor B. main C. nonessential D. unimportant
Mark the letter A, B, C, or D on your answer sheet to indicate the underlined part that needs correction in each of the following questions from 3 to 5.
Câu 3 (NB): My parents and I go usually to the zoo when we have free time.
A. My B. go usually C. when D. free time
Câu 4 (TH): Dreams commonly made up of either visual or verbal images.
A. commonly B. made up of C. either D. or
Câu 5 (VD): Globally and internationally, in the 1990’s stood out as the warmest decade in the history of weather records.
A. Globally and internationally B. stood out
C. warmest D. of
Phần 2
Mark the letter A, B, C, or D on your answer sheet to indicate the word(s) OPPOSITE in meaning to the underlined word(s) in each of the following questions from 6 to 7.
Câu 6 (TH): “That is a well-behaved boy whose behavior has nothing to complain about.”
A. behaving nice B. good behavior
C. behaving improperly D. behaving cleverly
Câu 7 (TH): We are now in a 24/7 society where shops and services must be available all hours.
A. an active society B. a physical society C. an inactive society D. a working society
Mark the letter A, B, C, or D on your answer sheet to indicate the sentence that best combines each of the pair of sentences in the following questions from 8 to 9.
Câu 8 (VD): Tim went on a two-day trip. He took more clothes than necessary.
A. Tim needn’t have taken so many clothes on a two-day trip.
B. Tim can’t have taken so many clothes on a two-day trip.
C. Tim couldn’t have taken so many clothes on a two-day trip.
D. Tim mustn’t have taken so many clothes on a two-day trip.
Câu 9 (VDC): John lent me money. Otherwise, I would have gone out of business.
A. I wouldn’t have gone out of business if John had lent me money.
B. Had it not been for John lending me money, I would have gone out of business.
C. Even if John lent me money, I went out of business.
D. John lent me money, but I went out of business.
Phần 3
Mark the letter A, B, C, or D on your answer sheet to indicate the most suitable response to complete each of the following exchanges from 10 to 11.
Câu 10 (TH): Two colleagues are talking with each other about their work at the office.
Tom: “Lucy! I got a promotion today!” Lucy: “ ”
A. Wow, this is great news! I am so glad for you.
B. If I want to lead, then I need to prove it.
C. Convince people of their value, just to lead.
D. Always set yourself outs as an example, do a good job. Câu 11 (NB): Tom: “Didn’t you go to the cinema last night?” Lucy: “ ”
A. Yes, I stayed at home. B. Ok. That’s a good idea.
C. No, it was too cold to go out. D. Yes, I lost the ticket.
Mark the letter A, B, C, or D on your answer sheet to indicate the word whose underlined part differs from the other three in pronunciation in each of the following questions from 12 to 13.
Mark the letter A, B, C, or D on your answer sheet to indicate the correct answer to each of the following questions from 14 to 27.
Câu 14 (TH): I have just found the book .
A. which you were looking B. you were looking
C. for that you were looking D. you were looking for
Câu 15 (TH): In the UK, seven is usually regarded the luckiest number while thirteen is the opposite.
A. like B. with C. for D. as
Câu 16 (VD): They sacrifices so that their only child could have a good education.
A. did B. provided C. made D. lent
Câu 17 (VD): To Michelle, her father is the greatest person in the world and he always sets a good
for her.
A. role B. action C. example D. behaviour
Câu 18 (TH): I
was stolen yesterday.
a bike to school every day but today I
to school by bus because it
A. ride – am going B. is riding – am going C. rode – went D. ride – go
Câu 19 (VD): Thanks to the AI applications, Internet users into a new language in real time.
A. can get webpages to translate B. can translate webpages
C. can have webpages translated D. can have webpages translate
Câu 20 (VD): At the level, you can join three-year or four-year colleges.
A. postgraduate B. primary C. undergraduate D. secondary
Câu 21 (TH): The lecturer recommended a number of books before the exam.
A. to have read B. to read C. we reading D. reading
Câu 22 (TH): Some Koreans believe that it’s impolite to eye contact with a person who has a high position.
A. put B. maintain C. lose D. show
Câu 23 (TH): Ellie asked Stan to look at the new catalogue.
A. whether he wants B. did he want C. do you want D. if he wanted
Câu 24 (VD): In Viet Nam, you shouldn’t at somebody house on the 1st day of the New Year unless you have been invited by the house owner.
A. put up B. go up C. show up D. get up
Câu 25 (TH): In the past, the and engagement ceremonies took place one or two years before the wedding.
A. proposing B. proposed C. proposal D. propose
Câu 26 (VD): Of the two bridesmaids, Lisa turned out to be .
A. more charming B. the least charming C. the more charming D. the most charming
Câu 27 (TH): Japanese manage to ask direct questions in order not to embarrass person who they are speaking with.
A. The – the B. A – a C. The – a D. A – the
Phần 4
Read the passage and mark the letter A, B, C, or D on your answer sheet to indicate the correct answer to each of the questions from 28 to 35.
Belgium is a very old country, with a fascinating mixture of old customs and modern laws. Belgium weddings may be performed as a civil ceremony or as a religious ceremony.
Traditionally, when a couple in Belgium wishes to announce their marriage, the wedding invitations are printed on two sheets of paper, one from the bride’s family and one sheet from the groom’s family. These wedding invitations symbolize the union of the two families and the partnership of the new union.
An ancient Belgium custom that is designed to unite the two families calls for the bride to stop as she walks up the aisle and to hand her mother a single flower. The two then embrace. Then, during the
recessional, the bride and groom walk to the groom’s mother and the new bride hands her new mother-in- law a single flower and the two of them embrace, symbolizing the bride’s acceptance of her new mother.
One of the most important and enduring traditions of the Belgium wedding is for the bride to carry a specially embroidered handkerchief that has her name embroidered on it. After the wedding this handkerchief is framed and hung on the wall in a place of honor. When the next female member of the bride’s family is to be wed, the handkerchief is removed from its frame, the new bride’s name is embroidered onto it, and it is passed down. The wedding handkerchief is passed from generation to generation, and is considered an important family heirloom.
During the wedding mass, the bride and the groom are enthroned in two large chairs placed near the altar, symbolizing that on this day and in this place they are the king and the queen. At the conclusion of the ceremony, the groom slips the wedding ring onto the third finger of his bride’s left hand. The ring, being an endless circle, symbolizes never-ending love, and the third finger of the left hand is believed to hold the vein that travels to the heart, symbolizing love. At the conclusion of the ceremony, the bride and groom share their first kiss as husband and wife. The kiss is considered a symbolic act of sharing each other’s spirit as the couple each breathes in a portion of their new mate’s soul.
The bridesmaids traditionally take up a collection of coins and as the bride and groom exit the church, the bridesmaids toss the coins to the poor outside the church. Giving gifts of money to the poor helps to insure prosperity for the new bride and groom.
Following the wedding the bride and groom are off on their honeymoon. In ancient times the honeymoon, which was celebrated by the drinking of mead, or honey wine, would last 28 days, one complete cycle of the moon. This was to make sure that the bride’s family did not try to steal their daughter back from her new husband.
(Adapted from http://www.best-country.com/)
Câu 28 (TH): The word “insure” in the paragraph 6 could be best replaced by .
A. express B. indemnify C. determine D. affirm
Câu 29 (TH): The following is true about Belgium’s wedding, EXCEPT .
A. The bride often hugs her mother-in-law before embracing her mother
B. The weddings in Belgium are not only a civil event but also a religious one
C. The wedding invitations are the symbol of both the bride’s and the groom’s families
D. Each mother of the couple is given a single flower in their children’s wedding
Câu 30 (TH): The author mentioned honeymoon in the past in the last paragraph as a period that .
A. lasts for a fortnight after wedding
B. the new couple serves the guests honey wine
C. the bride and the groom live far from each other
D. protects the new bride from her family’s effort to take her back
Câu 31 (TH): Which of the following could be the best title of this passage?
A. Belgium’s wedding customs and traditions
B. The bride’s and groom’s traditional activities on their wedding day
C. Belgium’s wedding ceremony
D. The differences between an ancient wedding and a modern one in Belgium
Câu 32 (VD): The word “heirloom” in paragraph 4 is closest in meaning to .
A. representation B. pride C. dowry D. inheritance
Câu 33 (VD): It can be inferred from the passage that the wedding handkerchief .
A. is highly appreciated in the home of Belgian people
B. is only replaced by another person in their house
C. is prepared for the bride by her mother before the wedding
D. is embroidered in most important occasions in Belgium
Câu 34 (TH): According to paragraph 5, what is CORRECT about the wedding ring?
A. The groom wears the ring for his mate at the beginning of the ceremony.
B. The ring represents the boundless love of the couple.
C. The ring is presented by the queen and the king of their country.
D. It is worn onto the third finger of the bride’s right hand.
Câu 35 (NB): What does the word “them” in the third paragraph refer to?
A. the groom and his mother-in-law B. the bride and the groom
C. the bride and her mother D. the bride and her mother-in-law
Read the passage and mark the letter A, B, C, or D on your answer sheet to indicate the correct answer to each of the questions from 36 to 40.
One way of training for your future occupation in Germany is by pursuing a dual vocational training
programme. Such programmes offer plenty of opportunity for on-the-job training and work experience. Programmes usually last between two and three and a half years and comprise theoretical as well as practical elements. You will spend one or two days a week, or several weeks at once, at a vocational school where you will acquire the theoretical knowledge that you will need in your future occupation. The rest of the time will be spent at a company. There you get to apply your newly acquired knowledge in practice, for example by learning to operate machinery. You will get to know what your company does, learn how it operates and find out if you can see yourself working there after completing your training.
This combination of theory and practice gives you a real head start into your job: by the time you have completed your training, you will not only have the required technical knowledge, but you will also have hands-on experience in your job. There are around 350 officially recognised training programmes in Germany, so chances are good that one of them will suit your interests and talents. You can find out which one that might be by visiting one of the jobs and vocational training fairs which are organised in many German cities at different times in the year.
Employment prospects for students who have completed a dual vocational training programme are very good. This is one of the reasons why this kind of training is very popular with young Germans: around two thirds of all students leaving school go on to start a vocational training programme.
(Source: http ://www. make-it-in-germany. com)
Câu 36 (NB): How many German school leavers choose this vocational training programme?
A. around one out of five B. less than a third
C. about 70% D. well over 75%
Câu 37 (NB): The word “it” in the first paragraph refers to .
A. organisation B. machinery C. knowledge D. company
Câu 38 (TH): Which of the following statements best describes the dual vocational training programmes?
A. These programmes provide you with both theoretical knowledge and practical working experience.
B. These programmes consist of an intensive theoretical course of two and a half years at a vocational school.
C. These programmes require you to have only practical working time at a certain company.
D. These programmes offer you some necessary technical skills to do your future job.
Câu 39 (TH): The word “hands-on” in the second paragraph is closest in meaning to .
A. practical B. technical C. theoretical D. integral
Câu 40 (TH): Which of the following is probably the best title of the passage?
A. Employment Opportunities and Prospects in Germany
B. Dual Vocational Training System in Germany
C. Combination of Theory and Practice in Studying in Germany
D. Higher Education System in Germany
Read the following passage and choose the best answer for each blank from 41 to 45.
Going Inside Black Holes
One of the strangest phenomena in the universe is the black hole. For years, (41) have studied black holes in an attempt to better understand how they function. Like vacuum cleaners, black holes will suck up anything (42) crosses their path. The incredible sucking power that black holes generate comes from gravity. They can quickly swallow up anything including planets, space debris, and anything else imaginable. Even light cannot escape the (43) _ of black holes. Since they are able to pull in light, black holes are nearly impossible to see even with high-powered telescopes.
(44) , scientists are able to detect the presence of black holes in space because of their effect on an observed area.
Black holes can originate in a few ways. One type of black holes occurs when a star comes to the end of its lifecycle and it dies in a supernova explosion. They can also occur when the mass of a neutron
star becomes so (45)
that it collapses in on itself. Black holes may also occur when several
large and dense stars collide with one another in space.
Câu 41 (TH): A. scientist B. scientific C. science D. scientists
Câu 42 (NB):
Câu 43 (TH): A. that
A. catch B. what
B. opportunity C. whose
C. achievement D. who
D. grasp
Câu 44 (TH):
Câu 45 (VD): A. Moreover
A. immense B. However
B. great C. In fact
C. huge D. Therefore
D. extreme
Mark the letter A, B, C, or D on your answer sheet to indicate the word that differs from the rest in the position of the primary stress in each of the following questions from 46 to 47.
Mark the letter A, B, C, or D on your answer sheet to indicate the sentence that is closest in meaning to each of the following questions from 48 to 50.
Câu 48 (VD): “Well done, Jerry, you’ve passed the driving test.”
A. I told Jerry that she had done well in her driving test.
B. I told that Jerry had passed her driving test.
C. I congratulated Jerry for passing her driving test.
D. I congratulated Jerry on passing her driving test.
Câu 49 (TH): My brother and I went to that school.
A. I went to that school and so my brother did.
B. I went to that school and so did my brother.
C. I went to that school and my brother, too.
D. I went to that school and so my brother did, too.
Câu 50 (VDC): If only you had told me the truth about the theft.
A. Had you had told me the truth, there wouldn’t have been the theft.
B. You only told me the truth if there was a theft.
C. Only if you has told me the truth about the theft.
D. You should have told me the truth about the theft.
Đáp án
1-C 2-B 3-B 4-A 5-A 6-C 7-C 8-A 9-B 10-A
11-A 12-B 13-A 14-D 15-D 16-C 17-C 18-A 19-C 20-C
21-D 22-B 23-D 24-C 25-C 26-C 27-A 28-B 29-A 30-D
31-A 32-D 33-A 34-B 35-D 36-C 37-D 38-A 39-A 40-B
41-D 42-A 43-D 44-B 45-B 46-B 47-B 48-D 49-B 50-D
Câu 1: Đáp án C Kiến thức: Thành ngữ Giải chi tiết:
stand one’s ground: giữ vững lập trường
LỜI GIẢI CHI TIẾT
A. felt sorry for us: cảm thấy tiếc cho chúng tôi
B. changed his decision: đã thay đổi quyết định của mình
C. refused to change his decision: từ chối thay đổi quyết định của mình
D. wanted to continue: muốn tiếp tục
=> stood his ground: giữ vững lập trường = refused to change his decision: từ chối thay đổi quyết định của mình
Tạm dịch: Mặc dù chúng tôi đã tranh cãi với anh ấy trong một thời gian dài, anh ấy vẫn giữ vững lập trường của mình.
Câu 2: Đáp án B
Kiến thức: Từ đồng nghĩa
Giải chi tiết:
core (adj): quan trọng, chính
A. minor (adj): nhỏ
B. main (adj): chính
C. nonessential (adj): không trọng yếu, không cần thiết
D. unimportant (adj): không quan trọng, không trọng đại
=> core (adj): quan trọng, chính = main (adj): chính
Tạm dịch: Tiếng Anh, Toán và Văn là những môn học chính, là các môn thi bắt buộc trong kỳ thi quốc gia.
Câu 3: Đáp án B
Kiến thức: Trạng từ tần suất
Giải chi tiết:
Trạng từ tần suất đứng trước động từ thường và sau động từ “to be” Sửa: go usually => usually go
Tạm dịch: Bố mẹ tôi và tôi thường đến sở thú khi chúng tôi có thời gian rảnh.
Câu 4: Đáp án A
Kiến thức: Câu bị động
Giải chi tiết:
Dấu hiệu: “Dreams” (giấc mơ) chịu tác động của hành động “make up of” (tạo thành) Câu bị động thì hiện tại đơn: S + am/ is/ are + Ved/ V3 + (by O).
Chủ ngữ “dreams” số nhiều => tobe chia “are” Sửa: commonly => are commonly
Tạm dịch: Giấc mơ thường được tạo thành từ hình ảnh trực quan hoặc bằng lời nói.
Câu 5: Đáp án A Kiến thức: Từ vựng Giải chi tiết:
globally (adv): toàn bộ, toàn cầu internationally (adv): trên bình diện quốc tế
globally = internationally => chỉ dùng 1 trong 2 từ, không kết hợp cả 2 Sửa: Globally and internationally => Globally
Tạm dịch: Trên toàn cầu, những năm 1990 là thập kỷ nóng nhất trong lịch sử ghi chép thời tiết.
Câu 6: Đáp án C
Kiến thức: Từ trái nghĩa
Giải chi tiết:
well-behaved (adj): có giáo dục, ngoan ngoãn
A. behaving nice: cư xử tốt
B. good behavior: ứng xử tốt
C. behaving improperly: cư xử không đúng mực
D. behaving cleverly: cư xử khéo léo
=> well-behaved (adj): có giáo dục, ngoan ngoãn >< behaving improperly: cư xử không đúng mực Tạm dịch: Đó là một cậu bé ngoan ngoãn, không có hành vi nào đáng phàn nàn. Câu 7: Đáp án C Kiến thức: Từ trái nghĩa Giải chi tiết: a 24/7 society: xã hội hoạt động 24/7 A. an active society: một xã hội hoạt động B. a physical society: một xã hội vật chất C. an inactive society: một xã hội không hoạt động D. a working society: một xã hội làm việc => a 24/7 society: xã hội hoạt động 24/7 >< an inactive society: một xã hội không hoạt động Tạm dịch: Chúng ta hiện đang ở trong một xã hội hoạt động 24/7, nơi các cửa hàng và dịch vụ phải có sẵn trong mọi giờ. Câu 8: Đáp án A Kiến thức: Động từ khuyết thiếu Giải chi tiết: needn’t have Ved/ V3: đáng lẽ không cần làm (nhưng đã làm) can’t/ couldn’t have Ved/ V3: chắc chắn đã không Không có dạng “mustn’t have + V_ed/V3) Tạm dịch: Tim tiếp tục một chuyến đi hai ngày. Anh mang nhiều quần áo hơn mức cần thiết. = Tim đáng lẽ không cần mang quá nhiều quần áo cho chuyến đi hai ngày. B. Tim chắc chắn đã không mang quá nhiều quần áo cho chuyến đi hai ngày. => sai về nghĩa
C. Tim chắc chắn đã không mang quá nhiều quần áo cho chuyến đi hai ngày. => sai về nghĩa
D. Sai ở “mustn’t have taken”
Câu 9: Đáp án B
Kiến thức: Đảo ngữ câu điều kiện loại 3
Giải chi tiết:
Cách dùng: Câu điều kiện loại 3 dùng để diễn tả một giả thiết trái ngược với thực tế đã xảy ra ở quá khứ Công thức chung: If S + had + Ved/ V3 + O, S + would/ could + have + Ved/ V3 + O.
Dạng đảo ngữ: Had + S + (not) + Ved/ V3, S + would/ could have + Ved/ V3.
Tạm dịch: John cho tôi mượn tiền. Nếu không thì, tôi đã ngừng việc kinh doanh rồi.
= Nếu John không cho tôi mượn tiền, tôi sẽ đã ngừng việc kinh doanh rồi.
A. Tôi sẽ không ngừng việc kinh doanh nếu John cho tôi mượn tiền. => sai về nghĩa
C. Thậm chí nếu John cho tôi mượn tiền, tôi cũng sẽ ngừng việc kinh doanh. => sai về nghĩa
D. John cho tôi mượn tiền, nhưng tôi ngừng việc kinh doanh. => sai về nghĩa
Câu 10: Đáp án A
Kiến thức: Ngôn ngữ giao tiếp
Giải chi tiết:
Hai đồng nghiệp đang nói chuyện với nhau về công việc của họ tại văn phòng.
Tom: “Lucy à! Hôm nay tôi được thăng chức!” Lucy: “ ”
A. Wow, đây là một tin tuyệt vời! Tôi rất mừng cho bạn.
B. Nếu tôi muốn lãnh đạo, thì tôi cần phải chứng minh điều đó.
C. Thuyết phục mọi người về giá trị của họ, chỉ để lãnh đạo.
D. Luôn đặt mình ra làm ví dụ, làm tốt công việc. Các phản hồi B, C, D không phù hợp với ngữ cảnh. Câu 11: Đáp án A
Kiến thức: Ngôn ngữ giao tiếp
Giải chi tiết:
Tom: “Tối qua bạn đã không đi xem phim đúng không?” Lucy: “ ”
A. Đúng, tôi ở nhà.
B. Được. Đó là một ý kiến hay.
C. Không, trời quá lạnh để đi ra ngoài.
D. Có, tôi bị mất vé.
Các phản hồi B, C, D không phù hợp với ngữ cảnh.
Câu 12: Đáp án B
Kiến thức: Phát âm “oo”
Giải chi tiết:
A. spoon /spuːn/
B. book /bʊk/
C. mood /muːd/
D. moon /muːn/
Phần gạch chân đáp án B phát âm là /ʊ/, còn lại là /uː/
Câu 13: Đáp án A
Kiến thức: Phát âm “-ed”
Giải chi tiết:
A. developed /dɪˈveləpt/
B. pretended /prɪˈtendɪd/
C. vibrated /vaɪˈbreɪtɪd/
D. visited /ˈvɪzɪtɪd/
Quy tắc:
Cách phát âm đuôi “ed”:
– Đuôi “ed” được phát âm là /ɪd/ khi động từ có phát âm kết thúc là /t/ hay /d/
– Đuôi “ed” được phát âm là /t/ khi động từ có phát âm kết thúc là /s/,/f/,/p/,/ʃ/,/tʃ/,/k/
– Đuôi “ed” được phát âm là /d/ với các trường hợp còn lại Phần gạch chân đáp án A phát âm là /t/, còn lại là /ɪd/
Câu 14: Đáp án D
Kiến thức: Đại từ quan hệ
Giải chi tiết:
Trong mệnh đề quan hệ:
– which: cái mà => thay thế cho một danh từ chỉ vật; đóng vai trò chủ ngữ/ tân ngữ; hoặc lược bỏ khi nó đóng vai trò làm tân ngữ trong mệnh đề quan hệ xác định
– that: người mà/cái mà => thay thế cho “who”, “whom”, “which” hoặc lược bỏ khi nó đóng vai trò làm tân ngữ trong mệnh đề quan hệ xác định; không dùng giới từ trước “that”
look (v): nhìn look for: tìm kiếm
Tạm dịch: Tôi vừa tìm thấy cuốn sách bạn đang tìm kiếm.
Câu 15: Đáp án D Kiến thức: Giới từ Giải chi tiết:
to be regarded as sth: được coi là
Tạm dịch: Ở Anh, số bảy thường được coi là con số may mắn nhất trong khi mười ba thì ngược lại.
Câu 16: Đáp án C
Kiến thức: Sự kết hợp từ
Giải chi tiết:
A. do – did: làm, hành động
B. provide – provided: cung cấp
C. make – made: chế tạo, sản xuất
D. lend – lent: cho vay
=> make sacrifices: hy sinh
Tạm dịch: Họ đã hy sinh để đứa con duy nhất của họ có thể có một nền giáo dục tốt.
Câu 17: Đáp án C
Kiến thức: Sự kết hợp từ
Giải chi tiết:
A. role (n): vai trò
B. action (n): hành động
C. example (n): ví dụ
D. behaviour (n): hành vi, ứng xử
=> set a good example: nêu gương tốt
Tạm dịch: Đối với Michelle, cha cô là người vĩ đại nhất thế giới và ông luôn làm tấm gương tốt cho cô.
Câu 18: Đáp án A
Kiến thức: Sự phối hợp thì
Giải chi tiết:
Thì hiện tại đơn:
Cách dùng: Thì hiện tại đơn dùng để diễn rả một hành động chung chung, tổng quát lặp đi lặp lại nhiều lần hoặc một sự thật hiển nhiên, một hành động diễn ra trong thời gian hiện tại.
Công thức chung: S + V(s/es). Thì hiện tại tiếp diễn:
Cách dùng: Thì hiện tại tiếp diễn dùng để diễn tả những sự việc xảy ra ngay lúc chúng ta nói hay xung quanh thời điểm nói và hành động còn tiếp tục diễn ra (hành động kéo dài trong thời gian ngắn)
Công thức chung: S + am/ is/ are + Ving.
Tạm dịch: Tôi đi xe đạp đến trường hàng ngày nhưng hôm nay tôi đi học bằng xe buýt vì xe đạp đã bị mất trộm ngày hôm qua.
Câu 19: Đáp án C
Kiến thức: Câu bị động với “have/get”
Giải chi tiết:
have/get sth Ved/ V3: có cái gì được làm bởi ai đó
Tạm dịch: Nhờ các ứng dụng AI, người dùng Internet có thể sử dụng trang web được dịch sang ngôn ngữ mới trong thời đại này.
Câu 20: Đáp án C Kiến thức: Từ vựng Giải chi tiết:
A. postgraduate (adj): sau đại học
B. primary (adj): nguyên, căn bản
C. undergraduate (adj): chưa tốt nghiệp
D. secondary (adj): thứ yếu
=> undergraduate level: bậc đại học postgraduate level: sau đại học (cao học)
Tạm dịch: Ở bậc đại học, bạn có thể theo học các trường cao đẳng ba năm hoặc bốn năm.
Câu 21: Đáp án D Kiến thức: to V/ Ving Giải chi tiết:
recommend + Ving: gợi ý làm gì
Tạm dịch: Giảng viên gợi ý đọc một số cuốn sách trước kỳ thi.
Câu 22: Đáp án B Kiến thức: Từ vựng Giải chi tiết:
A. put (v): để, đặt
B. maintain (v): giữ gìn, duy trì
C. lose (v): mất
D. show (v): cho xem, cho thấy
Tạm dịch: Một số người Hàn Quốc tin rằng thật bất lịch sự khi duy trì giao tiếp bằng ánh mắt với một người có vị trí cao.
Câu 23: Đáp án D
Kiến thức: Câu tường thuật câu hỏi
Giải chi tiết:
Công thức tường thuật câu hỏi “Yes/ No”: S1 asked S2 if/ whether + S2 + V(lùi một thì). want (hiện tại đơn) => wanted (quá khứ đơn)
Tạm dịch: Ellie hỏi Stan anh ta muốn xem danh mục mới không.
Câu 24: Đáp án C
Kiến thức: Cụm động từ
Giải chi tiết:
A. put up: đưa lên
B. go up: tăng lên
C. show up: đến, xuất hiện
D. get up: thức dậy
Tạm dịch: Ở Việt Nam, bạn không nên xuất hiện tại nhà của ai đó vào ngày mùng 1 trừ khi bạn được chủ nhà mời.
Câu 25: Đáp án C
Kiến thức: Cấu trúc song hành
Giải chi tiết:
Cấu trúc song hành: A and B (A, B cùng một từ loại: danh từ, động từ, tính từ)
Dấu hiệu: sau “and” (và) là danh từ “ engagement” (lễ đính hôn) => cần điền danh từ vào chỗ trống
A. proposing (adj): đề nghị, đề xuất
B. proposed (adj): đề nghị, đề xuất
C. proposal (n): sự đề nghị, sự đề xuất, sự cầu hôn
D. propose (v): đề nghị, đề xuất
Tạm dịch: Trước đây, lễ cầu hôn và lễ đính hôn diễn ra một hoặc hai năm trước đám cưới.
Câu 26: Đáp án C Kiến thức: So sánh hơn Giải chi tiết:
“Of the two” + N số nhiều, N (1 trong 2) + be + the + so sánh hơn: Trong số hai …. , ai đó/cái gì thì …. hơn.
charming (adj): duyên dáng => tính từ dài, dạng so sánh hơn và chủ ngữ đã xác định: the more charming
Tạm dịch: Trong số hai phù dâu, Lisa xuất hiện duyên dáng hơn.
Câu 27: Đáp án A Kiến thức: Mạo từ Giải chi tiết:
The + tính từ chỉ quốc tịch => chỉ những người của quốc gia đó
the + danh từ (nếu phía sau có mệnh đề bổ sung thông tin/xác định cho nó)
Sau “person” có mệnh đề quan hệ “who they are speaking to” => “person” đã được xác định
Tạm dịch: Người Nhật cố gắng tìm cách đặt câu hỏi trực tiếp để không làm xấu hổ người mà họ đang nói chuyện.
Câu 28: Đáp án B
Kiến thức: Từ đồng nghĩa
Giải chi tiết:
Từ “insure” trong đoạn 6 có thể được thay thế bởi từ . insure (v): đảm bảo
A. express (v): bày tỏ, biểu lộ
B. indemnify (v): bảo đảm, bồi thường
C. determine (v): xác định
D. affirm (v): khẳng định, xác nhận
Thông tin: Giving gifts of money to the poor helps to insure prosperity for the new bride and groom. Tạm dịch: Tặng quà bằng tiền cho người nghèo giúp đảm bảo sự thịnh vượng cho cô dâu và chú rể mới. Câu 29: Đáp án A
Kiến thức: Đọc hiểu
Giải chi tiết:
Cái nào sau đây là sự thật về đám cưới của Bỉ, NGOẠI TRỪ .
A. Cô dâu thường ôm mẹ chồng trước khi ôm mẹ
B. Các đám cưới ở Bỉ không chỉ là một sự kiện dân sự mà còn là một sự kiện tôn giáo
C. Lời mời đám cưới là biểu tượng của cả gia đình cô dâu và chú rể
D. Mỗi bà mẹ của cặp vợ chồng được tặng một bông hoa trong đám cưới của con cái họ
Thông tin: These wedding invitations symbolize the union of the two families and the partnership of the new union…. An ancient Belgium custom that is designed to unite the two families calls for the bride to stop as she walks up the isle and to hand her mother a single flower… Then, during the recessional, the bride and groom walk to the groom’s mother and the new bride hands her new mother-in- law a single flower and the two of them embrace, symbolizing the bride’s acceptance of her new mother.
Tạm dịch: Những lời mời đám cưới này tượng trưng cho sự hợp nhất của hai gia đình và sự hợp tác của cuộc hôn nhân mới… Một phong tục cổ xưa của Bỉ được thiết lập để đoàn kết hai gia đình kêu gọi cô dâu
dừng lại khi cô đến chỗ hòn đảo nhỏ và trao cho mẹ cô một bông hoa duy nhất… Sau đó, trong buổi giới thiệu, cô dâu và chú rể đi đến nhà mẹ chú rể và cô dâu mới trao cho mẹ chồng một bông hoa duy nhất và hai người họ ôm nhau, tượng trưng cho sự chấp nhận của cô dâu với mẹ mới.
Câu 30: Đáp án D Kiến thức: Đọc hiểu Giải chi tiết:
Tác giả đã đề cập đến tuần trăng mật trong quá khứ trong đoạn cuối như một khoảng thời gian mà
.
A. kéo dài hai tuần sau đám cưới
B. cặp vợ chồng mới phục vụ khách rượu mật ong
C. cô dâu và chú rể sống xa nhau
D. bảo vệ cô dâu mới khỏi nỗ lực lấy lại cô ấy từ gia đình.
Thông tin: In ancient times the honeymoon, which was celebrated by the drinking of mead, or honey wine, would last 28 days, one complete cycle of the moon. This was to make sure that the bride’s family did not try to steal their daughter back from her new husband.
Tạm dịch: Vào thời cổ đại, tuần trăng mật, được tổ chức bằng việc uống rượu cỏ hay rượu mật ong, sẽ kéo dài 28 ngày, một chu kỳ hoàn chỉnh của mặt trăng. Điều này là để đảm bảo rằng gia đình cô dâu không cố gắng đánh cắp con gái của họ từ người chồng mới.
Câu 31: Đáp án A Kiến thức: Đọc hiểu Giải chi tiết:
Tiêu đề phù hợp nhất cho bài đọc là gì?
A. Phong tục và truyền thống đám cưới của Bỉ
B. Các hoạt động truyền thống của cô dâu và chú rể trong ngày cưới của họ
C. Lễ cưới của Bỉ
D. Sự khác biệt giữa một đám cưới cổ xưa và hiện đại ở Bỉ
Thông tin: Belgium weddings may be performed as a civil ceremony or as a religious ceremony. Traditionally, when a couple in Belgium wishes to announce their marriage, the wedding invitations are printed on two sheets of paper, one from the bride’s family and one sheet from the groom’s family… In ancient times the honeymoon, which was celebrated by the drinking of mead, or honey wine, would last 28 days, one complete cycle of the moon. This was to make sure that the bride’s family did not try to steal their daughter back from her new husband.
Tạm dịch: Đám cưới của Bỉ có thể được thực hiện như một nghi lễ dân sự hoặc như một nghi lễ tôn giáo. Theo truyền thống, khi một cặp vợ chồng ở Bỉ muốn tuyên bố kết hôn, lời mời đám cưới được in trên hai tờ giấy, một từ gia đình cô dâu và một tờ từ gia đình chú rể… Vào thời cổ đại, tuần trăng mật, được tổ chức bằng việc uống rượu cỏ hay rượu mật ong, sẽ kéo dài 28 ngày, một chu kỳ hoàn chỉnh của mặt trăng.
Điều này là để đảm bảo rằng gia đình cô dâu đã không cố gắng đánh cắp con gái của họ từ người chồng mới.
Câu 32: Đáp án D
Kiến thức: Từ đồng nghĩa
Giải chi tiết:
Từ “heirloom” trong đoạn 4 đồng nghĩa với từ .
heirloom (n): đồ đạc gia truyền
A. representation (n): sự thay mặt, sự đại diện
B. pride (n): sự kiêu hãnh, sự hãnh diện
C. dowry (n): của hồi môn
D. inheritance (n): quyền thừa kế, gia tài
=> heirloom = inheritance
Thông tin: The wedding handkerchief is passed from generation to generation, and is considered an important family heirloom.
Tạm dịch: Khăn tay đám cưới được truyền từ thế hệ này sang thế hệ khác, và được coi là một đồ gia truyền quan trọng của gia đình.
Câu 33: Đáp án A Kiến thức: Đọc hiểu Giải chi tiết:
Có thể suy ra từ đoạn văn chiếc khăn cưới .
A. được đánh giá cao trong gia đình của người Bỉ
B. chỉ được thay thế bởi một người khác trong ngôi nhà của họ
C. được mẹ chuẩn bị cho cô dâu trước ngày cưới
D. được thêu trong những dịp quan trọng nhất ở Bỉ
Thông tin: The wedding handkerchief is passed from generation to generation, and is considered an important family heirloom.
Tạm dịch: Khăn tay đám cưới được truyền từ thế hệ này sang thế hệ khác, và được coi là một đồ gia truyền quan trọng của gia đình.
Câu 34: Đáp án B Kiến thức: Đọc hiểu Giải chi tiết:
Theo đoạn 5, điều ĐÚNG về nhẫn cưới là gì?
A. Chú rể đeo nhẫn cho người bạn đời của mình vào đầu buổi lễ.
B. Chiếc nhẫn tượng trưng cho tình yêu vô bờ bến của cặp đôi.
C. Chiếc nhẫn được trình bày bởi nữ hoàng và nhà vua của đất nước họ.
D. Nó được đeo vào ngón tay thứ ba của bàn tay phải của cô dâu.
Thông tin: The ring, being an endless circle, symbolizes never-ending love, and the third finger of the left hand is believed to hold the vein that travels to the heart, symbolizing love.
Tạm dịch: Chiếc nhẫn, là một vòng tròn vô tận, tượng trưng cho tình yêu không bao giờ kết thúc, và ngón thứ ba của bàn tay trái được cho là giữ tĩnh mạch đi đến trái tim, tượng trưng cho tình yêu.
Câu 35: Đáp án D Kiến thức: Đọc hiểu Giải chi tiết:
Từ “them” trong đoạn 3 thay thế cho?
A. chú rể và mẹ vợ
B. cô dâu và chú rể
C. cô dâu và mẹ đẻ
D. cô dâu và mẹ chồng
Thông tin: Sau đó, trong buổi giới thiệu, cô dâu và chú rể đi đến nhà mẹ chú rể và cô dâu mới trao cho mẹ chồng một bông hoa duy nhất và hai người họ ôm nhau, tượng trưng cho sự chấp nhận của cô dâu với mẹ mới.
Tạm dịch: Then, during the recessional, the bride and groom walk to the groom’s mother and the new bride hands her new mother-in- law a single flower and the two of them embrace, symbolizing the bride’s acceptance of her new mother.
Câu 36: Đáp án C Kiến thức: Đọc hiểu Giải chi tiết:
Có bao nhiêu người trẻ rời trường học ở Đức chọn chương trình đào tạo nghề này?
A. khoảng một phần năm
B. ít hơn một phần ba
C. khoảng 70%
D. cũng trên 75%
Thông tin: This is one of the reasons why this kind of training is very popular with young Germans: around two thirds of all students leaving school go on to start a vocational training programme.
Tạm dịch: Đây là một trong những lý do tại sao loại hình đào tạo này rất phổ biến với giới trẻ Đức: khoảng hai phần ba học sinh rời trường tiếp tục bắt đầu một chương trình đào tạo nghề.
Câu 37: Đáp án D Kiến thức: Đọc hiểu Giải chi tiết:
Từ “it” trong đoạn 1 ám chỉ .
A. organisation (n): tổ chức
B. machinery (n): máy móc
C. knowledge (n): kiến thức
D. company (n): công ty
Thông tin: You will get to know what your company does, learn how it operates and find out if you can see yourself working there after completing your training.
Tạm dịch: Bạn sẽ biết công ty của bạn làm gì, tìm hiểu cách thức nó hoạt động và tìm hiểu xem bạn có thể thấy mình làm việc ở đó sau khi hoàn thành khóa đào tạo của mình không.
Câu 38: Đáp án A Kiến thức: Đọc hiểu Giải chi tiết:
Phát biểu nào sau đây mô tả đúng nhất các chương trình đào tạo nghề kép?
A. Các chương trình này cung cấp cho bạn cả kiến thức lý thuyết và kinh nghiệm làm việc thực tế.
B. Các chương trình này bao gồm một khóa học lý thuyết chuyên sâu kéo dài hai năm rưỡi tại một trường dạy nghề.
C. Các chương trình này yêu cầu bạn chỉ có thời gian làm việc thực tế tại một công ty nhất định.
D. Các chương trình này cung cấp cho bạn một số kỹ năng kỹ thuật cần thiết để thực hiện công việc tương lai của bạn.
Thông tin: This combination of theory and practice gives you a real head start into your job: by the time you have completed your training, you will not only have the required technical knowledge, but you will also have hands-on experience in your job.
Tạm dịch: Sự kết hợp giữa lý thuyết và thực hành này mang đến cho bạn một khởi đầu thực sự trong công việc của bạn: khi bạn hoàn thành khóa đào tạo, bạn sẽ không chỉ có kiến thức kỹ thuật cần thiết mà còn có kinh nghiệm thực hành trong công việc.
Câu 39: Đáp án A
Kiến thức: Từ đồng nghĩa
Giải chi tiết:
Từ “hands-on” trong đoạn 2 đồng nghĩa với từ .
hands-on (adj): thực hành
A. practical (adj): thực hành
B. technical (adj): thuộc kỹ thuật
C. theoretical (adj): thuộc lý thuyết
D. integral (adj): toàn bộ, không thể thiếu
Thông tin: This combination of theory and practice gives you a real head start into your job: by the time you have completed your training, you will not only have the required technical knowledge, but you will also have hands-on experience in your job.
Tạm dịch: Sự kết hợp giữa lý thuyết và thực hành này mang đến cho bạn một khởi đầu thực sự trong công việc của bạn: khi bạn hoàn thành khóa đào tạo, bạn sẽ không chỉ có kiến thức kỹ thuật cần thiết mà còn có kinh nghiệm thực hành trong công việc.
Câu 40: Đáp án B Kiến thức: Đọc hiểu Giải chi tiết:
Tiêu đề nào sau đâu là tiêu đề phù hợp cho bài đọc?
A. Cơ hội việc làm và triển vọng tại Đức
B. Hệ thống đào tạo nghề kép ở Đức
C. Kết hợp lý thuyết và thực hành học tập tại Đức
D. Hệ thống giáo dục đại học ở Đức
Thông tin: Một cách đào tạo cho nghề nghiệp tương lai của bạn ở Đức là theo đuổi một chương trình đào tạo nghề kép… Triển vọng việc làm cho sinh viên đã hoàn thành chương trình đào tạo nghề kép là rất tốt. Tạm dịch: One way of training for your future occupation in Germany is by pursuing a dual vocational training programme… Employment prospects for students who have completed a dual vocational training programme are very good.
Câu 41: Đáp án D Kiến thức: Từ loại Giải chi tiết:
A. scientist (n): nhà khoa học
B. scientific (adj): thuộc khoa học, có tính khoa học
C. science (n): khoa học
D. scientists (n): các nhà khoa học
Dấu hiệu: vị trí cần điền là chủ ngữ, vì vậy cần một danh từ, do động từ “have” ở dạng số nhiều, nên chủ ngữ là danh từ số nhiều
For years, (41) scientists have studied black holes in an attempt to better understand how they function. Tạm dịch: Trong nhiều năm, các nhà khoa học đã nghiên cứu về các hố đen để cố gắng hiểu rõ hơn về cách hoạt động của chúng.
Câu 42: Đáp án A
Kiến thức: Đại từ quan hệ
Giải chi tiết:
Trọng mệnh đề quan hệ:
– that: thay thế cho “who”, “whom”, “which” hoặc lược bỏ khi nó đóng vai trò làm tân ngữ trong mệnh đề quan hệ xác định
– what + S + V (nghi vấn từ): cái gì
– whose + danh từ: thay cho danh từ/ tính từ sở hữu
– who: thay thế cho một danh từ chỉ người; đóng vai trò chủ ngữ/ tân ngữ “anything” (bất kì thứ gì) => chỉ vật => loại D
Sau chỗ trống là một động từ “cross” (đi qua) => loại B, C
Like vacuum cleaners, black holes will suck up anything (42) that crosses their path.
Tạm dịch: Giống như những chiếc máy hút bụi, các hố đen sẽ hút tất cả những gì đi qua quỹ đạo của chúng.
Câu 43: Đáp án D Kiến thức: Từ vựng Giải chi tiết:
A. catch (n): sự nắm lấy, sự đánh cá
B. opportunity (n): cơ hội
C. achievement (n): thành tựu
D. grasp (n): sự túm lấy, hút lấy (khiến di chuyển ra chỗ khác) Even light cannot escape the (43) grasp of black holes.
Tạm dịch: Ngay cả ánh sáng cũng không thể tránh được sức hút của các hố đen.
Câu 44: Đáp án B Kiến thức: Từ vựng Giải chi tiết:
A. Moreover, S + V: hơn nữa
B. However, S + V: tuy nhiên
C. In fact, S + V: thực tế
D. Therefore, S + V: vì vậy, do đó
Since they are able to pull in light, black holes are nearly impossible to see even with high-powered telescopes. (44) However, scientists are able to detect the presence of black holes in space because of their effect on an observed area.
Tạm dịch: Vì các hố đen có thể hút cả ánh sáng nên gần như không thể nhìn thấy chúng kể cả với kính thiên văn công suất lớn. Tuy nhiên, các nhà khoa học có thể xác định sự tồn tại của các hố đen trong không gian nhờ ảnh hưởng của chúng lên một khu vực quan sát được.
Câu 45: Đáp án B Kiến thức: Từ vựng Giải chi tiết:
A. immense (adj): bao la, rộng lớn => không dùng để miêu tả khối lượng
B. great (adj): to, lớn, vĩ đại
C. huge (adj): to lớn, đồ sộ => miêu tả kích thước, lượng (không đếm được, mang nghĩa bóng)
D. extreme (adj): vô cùng, cùng cực (về trình độ, mức độ,…)
They can also occur when the mass of a neutron star becomes so (45) great that it collapses in on itself. Tạm dịch: Chúng cũng có thể xuất hiện khi khối lượng của một ngôi sao nơtron trở nên lớn đến mức mà nó tự vỡ vụn.
Câu 46: Đáp án B
Kiến thức: Trọng âm từ có 3 âm tiết
Giải chi tiết:
A. represent /reprɪˈzent/
B. envelop /ɪnˈveləp/
C. volunteer /vɒlənˈtɪə/
D. interact /ɪntərˈækt/
Quy tắc: Những từ có tận cùng là đuôi “-eer” thường có trọng âm rơi vào chính nó Trọng âm đáp án B rơi vào âm tiết thứ hai, còn lại là âm thứ ba
Câu 47: Đáp án B
Kiến thức: Trọng âm từ có 2 âm tiết
Giải chi tiết:
A. invent /ɪnˈvent/
B. finish /ˈfɪnɪʃ/
C. support /səˈpɔːt/
D. involve /ɪnˈvɒlv/
Quy tắc: Những động từ có 2 âm tiết thường có trọng âm rơi vào âm tiết thứ hai. Ngoại lệ: ‘finish Trọng âm đáp án B rơi vào âm tiết thứ nhất, còn lại là âm thứ hai
Câu 48: Đáp án D
Kiến thức: Câu tường thuật
Giải chi tiết:
Câu trực tiếp: “Well done, S + have/ has + Ved/ V3.”, S1 said to S2.: Làm tốt lắm…. Câu tường thuật: S1 + congratulated S2 + on V_ing.: Ai đó chúc mừng ai về việc gì Tạm dịch: “Làm tốt lắm Jerry, bạn đã vượt qua bài kiểm tra lái xe.”
= Tôi chúc mừng Jerry đã vượt qua bài kiểm tra lái xe của mình..
A. Tôi nói với Jerry rằng cô ấy đã hoàn thành tốt bài kiểm tra lái xe của mình. => sai về nghĩa
B. Tôi nói rằng Jerry đã vượt qua bài kiểm tra lái xe của mình. => sai về nghĩa
C. Sai. vì “congratulate sbd on sth”
Câu 49: Đáp án B Kiến thức: Đảo ngữ Giải chi tiết:
Câu đồng tình khẳng định:
– so + trợ V/ to be + S.
– S + V/ to be, too.
Tạm dịch: Tôi và anh tôi đã đi đến trường đó.
= Tôi đã đi đến trường đó và anh trai tôi cũng vậy.
A. sai vì “so my brother did” không đảo ngữ
C. sai vì “my brother, too” thiếu động từ
D. sai vì “so my brother did” không đảo ngữ và đã dùng “so” thì không dùng “too”
Câu 50: Đáp án D
Kiến thức: Câu đồng nghĩa, động từ khuyết thiếu
Giải chi tiết:
If only + S + had Ved/ V3: Giá mà ai đó đã làm gì trong quá khứ should have Ved/ V3: đáng lẽ nên làm (nhưng đã không làm) Tạm dịch: Giá như bạn đã nói với tôi sự thật về vụ trộm.
= Bạn đáng lẽ ra nên nói với tôi sự thật về vụ trộm.
A. Sai ở phần đảo ngữ trong câu điều kiện loại 3 “Had you had told me the truth”
B. Bạn chỉ nói với tôi sự thật nếu có một vụ trộm. => sai về nghĩa
C. Chỉ khi nào mà bạn đã nói với tôi sự thật về vụ trộm. => sai về nghĩa, sai “has”