How to use in-sentence of “semantic”:
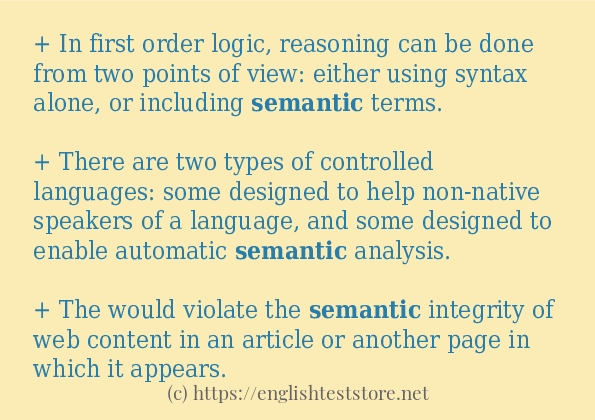
+ In first order logic, reasoning can be done from two points of view: either using syntax alone, or including semantic terms.
+ There are two types of controlled languages: some designed to help non-native speakers of a language, and some designed to enable automatic semantic analysis.
+ The would violate the semantic integrity of web content in an article or another page in which it appears.
+ Likewise, any semantic extension of a preexistent word, morpheme or locution..
+ The semantic web involves using Resource description Framework that has data that computers use.
Example sentences of “semantic”:
+ Chinese character components, whether semantic or phonetic in role, are the building blocks for all ChinaChinese Hanzi as well as in the derived forms of Vietnamese Chữ nôm and Chữ nho.
+ A more complex is the character 媽 "mā" meaning “mother”, in which the left part 女 "nǚ" meaning "woman" or "female" happens to be the semantic component, and also the section header under which dictionaries list the graph.
+ Chinese character components, whether semantic or phonetic in role, are the building blocks for all ChinaChinese Hanzi as well as in the derived forms of Vietnamese Chữ nôm and Chữ nho.
+ A more complex is the character 媽 “mā” meaning “mother”, in which the left part 女 “nǚ” meaning “woman” or “female” happens to be the semantic component, and also the section header under which dictionaries list the graph.
+ This template “should” be used where the content is being rendered in monospaced text for purely stylistic/display reasons, where this display has no particular semantic significance.
+ The Semantic Web is an idea of the inventor of the World Wide Web, Tim Berners Lee.
+ Chains of abstractions can therefore be constructed moving from neural impulses arising from sensory perception to basic abstractions such as color or shape to experiential abstractions such as a specific cat to semantic abstractions such as the “idea” of a CAT to classes of objects such as “mammals” and even categories such as “object” as opposed to “action”.
+ Other section headers are merely chosen for convenience of finding the character in a dictionary, and play neither a semantic nor a phonetic role, like 二 “èr” “two” in 亞 “yà” “second” or “inferior”,亅 “jué” in 了 “liào” “past tense marker”, and 一 “yī” “one” in 丁 “dīng” “fourth”.
+ Flynn effects on sub-factors of episodic and semantic memory: parallel gains over time and the same set of determining factors.
+ This permits backing out the logical change, but few storage systems provide an atomic write semantic on a RAID disk.
+ It is a word made of different parts; it has the phonetic part of “快”, which means “quick”, and a semantic part, 竹, meaning bamboo.
+ Sally Barr Ebest “Writing from A to Z: the easy-to-use reference handbook” 1999– Page 449 “A neologism is a newly coined word or phrase or a new usage of an existing word or phrase.” Lynne Bowker, Jennifer Pearson “Working With Specialized Language” 2002 Page 214 “Neologisms can also be formed in another way, however, by assigning a new meaning to an existing word.” The process of using a word in such a new context is sometimes called a semantic extension.
+ However, not all section headers function in a particular character as the semantic component.
+ But a rule of inference’s action is purely syntactic, and does not need to preserve any semantic property: any function from sets of formulae to formulae counts as a rule of inference.
